ForU AI: The Evolution of AI Agents in Web3

Abstract
ForU AI integrates artificial intelligence with blockchain, enabling autonomous AI agents to operate on-chain with decentralized identity and tokenized incentives. By leveraging Web3 infrastructure, these agents can transact, manage assets, and execute smart contracts without intermediaries. This approach enhances automation, transparency, and user ownership in digital economies.
As AI adoption accelerates, ForU AI positions itself at the forefront of this evolution, offering self-sustaining AI agents optimized for DeFi, governance, and personalized services. This paper outlines ForU AI’s core technology, market relevance, and competitive positioning, highlighting its role in shaping the future of decentralized AI-driven ecosystems.
Key Takeaways (TL;DR)
- AI x Blockchain Synergy – ForU AI combines artificial intelligence with blockchain to create autonomous, on-chain AI agents that can transact, manage assets, and execute smart contracts.
- Decentralized Identity & Data Ownership – AI-DID and Community-DID enable AI agents to operate with verifiable identities, ensuring transparency, security, and user control over data.
- Tokenized Incentives & Economic Sustainability – AI agents are financially aware, earning and spending tokens to sustain themselves, optimizing their actions based on economic incentives.
- Real-World Applications – ForU AI agents are designed for DeFi automation, DAO governance, and personalized Web3 services, reducing human coordination while enhancing efficiency.
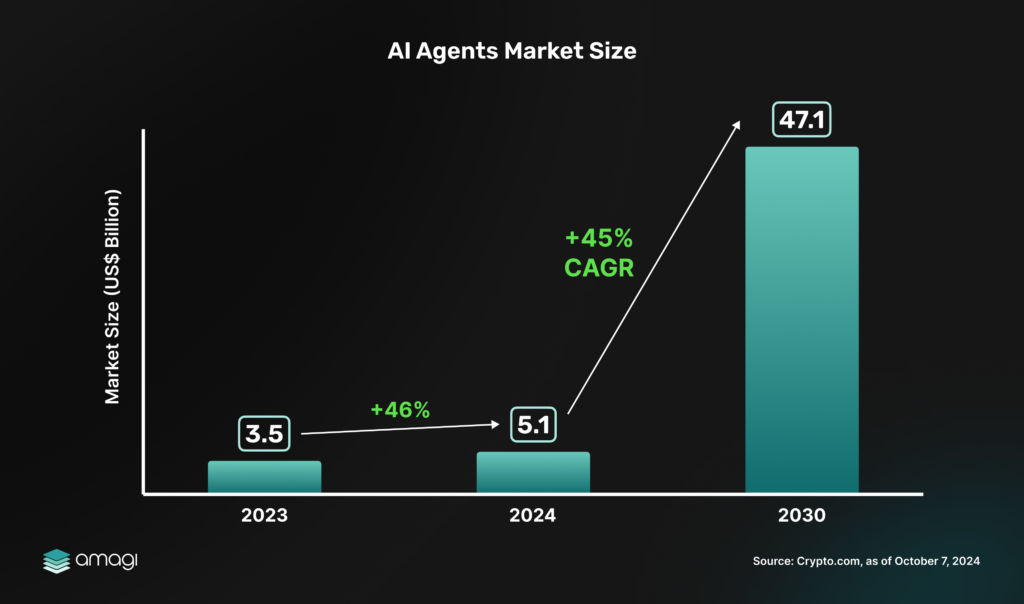
- Market Opportunity & Growth Potential – The AI-agent market is projected to grow from $5.1 billion in 2024 to $47.1 billion by 2030, positioning ForU AI as an innovator in decentralized AI automation.
1. Introduction
The AI agent industry is experiencing rapid growth, particularly in the crypto sector, where automation and decentralized intelligence are becoming critical. In 2024, the global AI agent market is valued at $5.1 billion and is projected to reach $47.1 billion by 2030, growing at a 45% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This expansion is fueled by AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data, optimize decision-making, and automate tasks, making it highly relevant for blockchain-based ecosystems.
Figure 1: AI Agents Market Size
However, despite its potential, AI integration in crypto faces significant challenges. Security risks remain a major concern, as AI-driven automation can be exploited if not properly managed. Ethical concerns, such as bias in AI models and transparency in decision-making, continue to raise questions. Additionally, computational complexity presents technical limitations, as deploying advanced AI models on decentralized infrastructure requires significant resources.
1.1 What is ForU AI?
ForU AI is a pioneering platform that integrates Real-World AI (RWAI) within a decentralized ecosystem of AI agents, enabling users to create and train their own autonomous AI agents on the blockchain. In essence, ForU AI merges advanced AI with Web3 infrastructure so that these AI agents can operate on-chain as independent entities. By leveraging blockchain, ForU’s AI agents gain the ability to own digital assets, execute smart contracts, and interact in a trustless ecosystem. This empowers individuals and communities to deploy AI agents that can transact and collaborate without centralized control. These agents can represent user interests online – whether managing community tasks, executing financial transactions, or personalizing services – all under user guidance but with a high degree of autonomy. ForU’s approach positions AI agents as key actors in the Web3 world, bringing together artificial intelligence and decentralized technologies in a single ecosystem.
1.2 Why Now? – AI x Crypto Synergy
The convergence of AI and blockchain is reaching a tipping point. Recent advances in generative AI and agentic AI (popularized by tools like ChatGPT) have shown how capable autonomous programs can be. At the same time, blockchain and cryptocurrencies have matured to enable trustless, programmable economies. Industry experts predict that “by 2027, half of companies that use generative AI will have launched ‘agentic AI’” – autonomous AI agents that act on behalf of users or businesses. This trend underscores a growing recognition that AI agents are the next big innovation wave. Blockchain catalyzes this wave’s sustainability: it provides a public, tamper-proof infrastructure where AI agents can operate transparently and transact value. Analysts note that the combination of AI and crypto, while nascent, is “rapidly evolving” and could even lead to a crypto-powered decentralized internet in the long run. In simpler terms, AI needs a secure, open environment to thrive beyond centralized servers – and crypto provides exactly that, from digital currencies for machine-to-machine payments to decentralized identity for trust.
Figure 2: The Exponential Growth of Online Data Due in Part to AI and Blockchain

The synergy between AI and blockchain redefines how we interact with technology and finance. ForU AI is seizing this moment by uniting these domains: as AI agents become more intelligent and autonomous, having them on-chain means they can directly participate in economic activities (like trading, investing, or content creation) without intermediaries. This synergy opens up “self-driving” digital economies where AI agents do the heavy lifting and humans set the goals. The timing is ideal because public awareness and comfort with AI is high, and the Web3 infrastructure (smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs, etc.) is robust enough to support complex autonomous operations. ForU AI stands at this intersection of trends, aiming to demonstrate that AI agents + crypto = a powerful new paradigm for technology and business.
1.3 Who is Behind ForU AI?
ForU AI is led by a team with deep experience in blockchain and AI domains. The project’s founder and CEO is Pang Xue Kai, best known as the ex-founder and CEO of Tokocrypto (one of Southeast Asia’s largest cryptocurrency exchanges). Under his leadership, the team’s vision strongly focuses on user empowerment, data ownership, and bridging Web2 and Web3. “At ForUAI, we’re not just creating a platform; we’re championing a movement to ensure individuals retain control over their personal data and are rightfully compensated for its use,” Pang Xue Kai has stated, emphasizing principles of user consent and reward (Litepaper ForuAI | 4UAI Litepaper). This vision translates into ForU’s mission: to bring people’s ideas, communities, and passions on-chain through AI so that everyone can benefit from AI technology, not just big corporations. The ForU AI team includes experts in artificial intelligence, blockchain engineering, and data security, many of whom have backgrounds in successful tech startups. Backed by prominent investors (such as DWF Labs, GSR Ventures, IBC Group, Blum Labs, WAGMi Ventures, NLS Ventures, TRIVE Digital, 1982 Venture, and other notable angel investors), the team has the resources and strategic support to execute its ambitious roadmap.
2. ForU AI: Core Technology & Ecosystem
2.1 AI Agents & Their Unique Attributes
AI Agents in Web3 – Autonomous, Data-Driven, Evolving: In the context of Web3, an AI agent is an autonomous digital entity that can perceive data, make decisions, and execute actions on blockchain networks without constant human oversight. Unlike a simple script or bot, an AI agent has a degree of “agency” – it can learn from experience and adapt its behavior to better achieve its assigned goals. ForU AI’s agents epitomize this concept. They operate as on-chain actors, holding blockchain wallets, interacting with smart contracts, and responding to real-time data. Because they are data-driven (often powered by machine learning models), they improve over time as they process more information. For example, a community management AI agent might analyze which types of posts engage a community and then adjust its content strategy accordingly. These agents are particularly suited for Web3 because they are embedded in a trustless environment – all their transactions and decisions can be transparent and governed by code. This ensures accountability (their actions are on the ledger) and security (they cannot be easily tampered with by malicious third parties).
In practical terms, a Web3 AI agent could be considered a digital coworker or assistant that runs 24/7: it could invest cryptocurrency on your behalf, moderate your decentralized forum, or even negotiate deals in a marketplace, all according to the parameters you set. Because they live on-chain, they can own and exchange assets directly – something traditional AI agents (running on a server) cannot easily do. This native presence in a crypto economy is a game-changer. It enables AI agents to raise their own funds, pay for services (like API calls or additional data), and execute agreements via smart contracts.
Key Differentiators of ForU AI’s Agents: ForU AI’s approach to AI agents includes several unique attributes that set it apart from earlier generations of AI bots or agent platforms. Three core differentiators are:
- Monetary Awareness: ForU AI agents are designed with financial reasoning and blockchain wallets, enabling them to manage budgets, assess costs vs. benefits, and prioritize tasks based on economic incentives. This allows agents to sustain themselves—spending tokens on data or computing power when beneficial. As Pang Xue Kai noted, the vision is that agents will “support their own computational needs,” paying for consumed resources. Unlike typical AI systems with unlimited lab resources, ForU’s agents treat resources as scarce commodities. By autonomously earning and spending cryptocurrency—offering paid services to earn tokens and reinvesting in upgrades—they create a self-sustaining loop where successful agents thrive.
- “Survival of the Fittest” via Performance: ForU’s AI agents operate in a competitive, gamified environment where only those that effectively meet real-world KPIs continue to receive resources. This creates an evolutionary dynamic: agents that learn and adapt faster improve over time, while underperformers must pivot or risk obsolescence. By continuously testing agents against key benchmarks like profit, user engagement, or decision accuracy, ForU ensures its ecosystem grows more intelligent and effective. Since agents must budget resources, those that misallocate tokens will “go broke,” while successful ones accumulate capital to reinvest—driving a self-optimizing AI network where the best strategies prevail.
- Decentralized Identity Integration: ForU AI agents are enriched with decentralized identity (DID) data from ForU’s AI-DID and Community-DID systems, ensuring they operate with verifiable identities. AI-DID serves as a digital “passport,” storing credentials on the blockchain, while Community-DID links agents to specific groups or networks. This allows agents to represent communities authentically—for instance, a sports fan AI might carry a token or NFT proving its affiliation. DID also enhances trust, enabling users and agents to verify identities on-chain, reducing risks from rogue AI. Additionally, agents can access personalized data (with consent), tailoring services based on secure, private user preferences. Unlike other AI frameworks, ForU’s agents have defined roles (via Community-DID) and controlled access to knowledge (via AI-DID), making them more socially integrated and purpose-driven than generic AI programs.
In summary, ForU AI’s agents are not generic chatbots – they are autonomous economic actors (monetary awareness), engaged in a continuous improvement contest (performance-driven evolution), and grounded in the Web3 identity fabric (AI-DIDs). These differentiators ensure that the agents are self-sufficient, continuously improving, and trustworthy. As Pang Xue Kai highlighted, “unlike previous AI Agents,” which might simply chat or perform tasks, ForU’s agents are money-smart, goal-driven, and identity-aware from day one. This combination makes them far more effective and aligned with user needs in the decentralized future.
2.2 The Three Pillars of ForU AI
ForU AI’s ecosystem is built on three foundational pillars enabling its decentralized AI network vision. These are AI-DID, Community-DID, and AI Agents – each playing a distinct role in the network’s architecture. Below, we break down each pillar and its function:
- AI-DID (Artificial Intelligence – Decentralized Identity): is a verifiable, on-chain identity for ForU AI users, aggregating consented data—such as social insights, activity, and preferences—secured cryptographically on the blockchain. Acting as a personal data vault, it enables hyper-personalization by allowing AI to tailor services based on user-approved information. As a DID, it remains user-controlled and trustless, ensuring only the user decides what’s included, while third parties can verify claims without relying on a central authority. Creating an AI-DID involves linking accounts securely, allowing the AI to understand a user’s digital footprint while preserving privacy. It also integrates Proof of Humanity and data ownership features, enabling users to earn rewards when their data is used. AI-DID is the foundation for AI-enhanced, blockchain-secured identities, empowering individuals with personalized, verifiable credentials.
- Community-DID: This concept extends decentralized identity to groups, communities, or public figures, authenticating and unifying their presence on the ForU AI network. A Community-DID acts as a verifiable identity—such as an NFT or token—that AI agents recognize as proof of membership. ForU AI ensures authenticity, allowing agents to represent official communities with cryptographic verification. This builds trust and structure within the AI network. ForU has launched Community-DIDs for ten groups, enabling users to create AI agents aligned with their communities. Essentially, Community-DID connects individuals to a larger entity, ensuring AI agents understand communal context and goals. This is key for SocialFi, where decentralized identity fosters trust. If AI-DID is a personal ID, Community-DID is a club membership, allowing AI agents to act as community coordinators or ambassadors.
- AI Agents: The third pillar is the AI agents themselves – the autonomous digital entities we’ve been discussing. They are the active participants that utilize the data from AI-DIDs and the context from Community-DIDs to perform tasks and transactions on-chain. These are “self-learning digital entities transacting on-chain,” essentially the workforce of the ForU AI network. Each AI Agent in ForU’s system is instantiated with certain goals (often derived from the user or community it serves) and equipped with the AI models and web3 access needed to accomplish those goals. The agents execute on behalf of users and communities: they might trade tokens, moderate chats, launch community proposals, scan for security threats, or interface with other dApps. Crucially, ForU’s agents are on-chain agents. They have their own decentralized identifiers and wallets, enabling them to send blockchain transactions like any user. This means an AI Agent could, for example, move funds from one DeFi protocol to another to optimize yield or automatically purchase an NFT that fits a user’s interests – all under programmed guidelines.
ForU AI’s core technology rests on Decentralized Identities (for users and communities) and AI Agents working in harmony. The AI-DID gives each user a private, monetizable data profile, the Community-DID provides a bond of trust and authenticity among groups, and the AI Agents are the autonomous executors that turn those identities and data into real actions and services on the blockchain.
Figure 3: How ForU AI Works – Current Features & Future Roadmap
2.3 Real-World Applications
ForU AI’s technology isn’t just theoretical – it’s being applied to solve real problems and automate complex tasks in the decentralized space. By combining AI-driven intelligence with on-chain execution, ForU’s AI Agents unlock new possibilities across various sectors of Web3. Here are some real-world applications emerging from the ForU AI ecosystem:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Automation: ForU AI agents serve as on-chain financial assistants, managing liquidity pools, yield farming, and token launches. Users can create tokens and liquidity pools, with AI handling the logistics—deploying contracts, adding liquidity, adjusting parameters, and executing trades for price stability. This automation lowers entry barriers for projects lacking financial expertise and enhances efficiency, as AI operates 24/7. Additionally, agents can scan for arbitrage opportunities or optimize lending strategies in seconds, executing transactions via smart contracts for seamless DeFi management.
- DAO Governance and Community Management: ForU AI agents act as 24/7 facilitators in DAOs and online communities, welcoming members, answering questions, and enforcing guidelines. They streamline governance by summarizing discussions, drafting proposals, tallying votes, and suggesting budget allocations. This automation keeps communities active without over-relying on human moderators. AI agents also boost engagement by tagging users for relevant proposals and evolving their strategies based on feedback and performance metrics, continuously improving as community managers.
- Digital Identity & Personalized Services: ForU leverages decentralized identity to give users control over their data, enabling personalized AI services. AI-DIDs allow agents to act as digital twins, understanding preferences, health, and financial habits (with consent) to interact with services on the user’s behalf. This includes Web3 single sign-on, personalized offers, and automated transactions. Users are rewarded in tokens for data sharing, incentivizing participation. With 8 million users already engaging with ForU’s mini-app, AI agents take personalization further by curating content and executing on-chain transactions. In the decentralized data economy, they can also help users safely sell or rent data via smart contracts, ensuring privacy and fair compensation—shifting power from big tech to individuals.
Figure 4: ForU AI Agent Use Cases: Automating Web3 Growth & Governance
Overall, the real-world applications of ForU AI span from finance to governance to personal life. By infusing AI into on-chain activities, they are streamlining processes that used to require lots of human coordination or were impossible to automate. ForU AI’s platform essentially provides a toolkit for building these real-world applications on top of its three pillars, establishing a new era of AI-driven automation in Web3.
3. Crypto as the Currency for AI
ForU AI believes cryptocurrency and blockchain are fundamental to enabling autonomous AI agents. In this ecosystem, crypto isn’t just a feature—it’s the foundation that allows AI to function independently. Blockchain enables trustless payments, microtransactions, and incentive structures that make AI-driven economies viable.
3.1 Why Blockchain is Essential for AI Economies
Traditional AI systems are confined to centralized platforms—they can’t hold money, own assets, or enter contracts. Blockchain changes this by providing an open, decentralized financial and computing infrastructure. With a cryptographic key, AI agents can hold wallets, execute smart contracts, and own tokenized assets, making them economic actors rather than passive tools.
ForU AI equips each agent with a crypto wallet, allowing seamless transactions. Blockchain’s transparency ensures every AI action is recorded, providing accountability and traceability. Decentralization also prevents censorship—unlike traditional financial systems, no single entity can freeze an agent’s funds or shut it down arbitrarily.
3.2 Trustless Payments & Microtransactions
AI agents often conduct frequent, small-scale transactions, such as retrieving data, tipping other agents, or charging micro-fees for services. Traditional payment systems are slow, costly, and require intermediaries, making them impractical for AI-driven economies. Cryptocurrencies, particularly on efficient blockchains like Sei, enable near-instant, low-cost microtransactions without third-party control.
This capability fuels machine-to-machine commerce. An AI agent can autonomously pay for milliseconds of decentralized cloud computing, purchase data, or distribute rewards—all governed by smart contracts. This automation allows large-scale AI networks to function seamlessly, handling thousands of transactions daily without human intervention. It also enables direct, trustless compensation for users and developers who train AI models, receiving automatic token rewards based on performance.
3.3 AI Incentives & Tokenized Models
The $FORU token underpins ForU AI’s ecosystem, aligning incentives for users, developers, and AI agents. It serves multiple functions: paying for advanced AI features, enabling governance participation, and rewarding contributors. Airdrops and staking mechanisms encourage early adoption, fueling network effects that enhance AI capabilities over time.
ForU’s AI Launchpad enables users to tokenize AI agents, allowing them to raise funds and create stakeholder communities invested in an agent’s success. Governance is also decentralized, with $FORU holders voting on ecosystem rules, feature integrations, and AI operational guidelines, ensuring no single entity unilaterally controls the system.
4. Foru AI Tokenomics and Governance
ForU AI’s economic framework is built around FORU, the native token that powers transactions, incentivizes user participation, and facilitates decentralized governance. Unlike centralized AI models where data monetization benefits corporations, ForU AI introduces a token-driven economy that aligns incentives between users, AI agents, and platform growth.
4.1 Token Utility
The $FORU token serves as the backbone of the ForU AI ecosystem, providing multiple utilities that drive adoption and sustainability:
- Transactional Utility: $FORU is used for payments within the ecosystem, including AI agent services, access to premium features, and data-sharing rewards. Its demand grows as more users and businesses integrate with the platform.
- Incentive Mechanism: Users earn $FORU tokens by contributing data in a privacy-preserving manner, ensuring that participants are fairly rewarded for engaging with AI-driven monetization models.
- Governance: Token holders gain voting rights in a decentralized governance structure, allowing them to shape platform policies, token supply decisions, and strategic developments.
4.2 Governance Framework
ForU AI employs a community-driven governance model, ensuring decentralized decision-making and long-term stakeholder alignment. The governance structure includes:
- Proposal Submission: Any holder meeting the minimum token requirement can submit governance proposals for platform upgrades, funding allocations, or economic adjustments.
- Voting Mechanism: Decisions are made through an on-chain voting process, where the number of FORU tokens held determines voting power, preventing centralized control while ensuring stakeholder influence.
- Execution & Oversight: Approved proposals are implemented by the core team with community monitoring, ensuring accountability and adherence to decentralized governance principles.
4.3 Economic Sustainability
To maintain long-term stability and value appreciation, ForU AI incorporates a structured economic model with sustainability measures:
- Capped Token Supply: FORU has a fixed supply to prevent inflation and ensure long-term value retention.
- Revenue Redistribution: Transaction fees are partially reinvested into ecosystem development, liquidity incentives, and user rewards, fostering continuous platform growth.
- Self-Sustaining Economy: The balance of transactional utility, staking rewards, and governance participation creates a circular economic model, ensuring incentives remain aligned across all ecosystem participants.
5. Competitive Positioning & Market Outlook
ForU AI operates in a rapidly growing AI-agent ecosystem, where decentralization and user data ownership are key differentiators. ForU AI empowers individuals with control over their data, enabling AI agents to operate autonomously in blockchain ecosystems. This chapter explores ForU AI’s competitive positioning, the transformation it brings compared to existing systems, and its roadmap for the future.
5.1 How ForU AI Stands Out Among AI-Agent Platforms
While several projects operate in the decentralized AI and data economy space, ForU AI differentiates itself through AI-driven identity solutions, decentralized data monetization, and a privacy-first approach. The table below highlights key comparisons.
Figure 5: ForU AI vs. Other AI Agent Platforms – Competitive Landscape
ForU AI positions itself at the intersection of AI autonomy, user ownership, and decentralized economic participation. Unlike competitors that focus on social engagement (Virtuals), compliance-driven AI (Olas), or enterprise AI integrations (Holoworld), ForU AI ensures that users and AI agents are economic participants rather than passive tools controlled by external platforms.
The biggest differentiator lies in how value circulates within the ecosystem. Many AI-agent projects still operate in semi-centralized models, where data is shared with platforms or governed by institutional structures. ForU AI shifts this paradigm by implementing AI-DID and decentralized governance, ensuring that users retain full control over data monetization, identity, and AI-driven automation.
As AI becomes more integrated into blockchain ecosystems, the ability to align incentives between AI agents, users, and governance mechanisms will determine which platforms thrive. While some competitors prioritize AI functionalities or specific enterprise solutions, ForU AI takes a broader, more sustainable approach by combining decentralized identity, financial autonomy, and AI-driven decision-making.
5.2 Future Growth and Expansion Potential
ForU AI’s expansion is driven by strategic partnerships, strong market traction, and a scalable user base, positioning it for long-term adoption in AI and Web3 ecosystems.
5.2.1 Strategic Partnerships & Market Reach
ForU AI’s collaboration with Blibli, Indonesia’s leading e-commerce platform, has resulted in a 40% increase in user engagement through AI-driven recommendations. This partnership also provides access to 17 million active shoppers, significantly expanding ForU AI’s market reach.
Additionally, ForU AI benefits from deep connections with Tokocrypto, allowing it to tap into an existing 5 million crypto users network. Many of these users are already familiar with tokenized incentives and decentralized finance, accelerating adoption.
5.2.2 Proven Market Traction & Adoption
Since its beta launch, ForU AI has experienced substantial adoption, marked by strong user growth, an expanding community, and increased activity in AI agents and AI-DID generations.
Figure 6: Market Traction and Adoption Metrics for ForU AI
The rapid adoption of ForU AI, mainly through its integration with the hyper-personalization platform Untukmu.AI, highlights the growing demand for AI-powered identity solutions and tokenized data monetization. This momentum reinforces ForU AI’s scalability as it expands into broader AI and Web3 applications. By enhancing user engagement with AI-driven recommendations and data insights, these integrations enable:
- AI-powered data processing, creating personalized user profiles.
- Tailored content and product recommendations, solving the Cold Start Problem in digital interactions.
- User-controlled data ownership allowing individuals to monetize their insights transparently.
5.2.3 Expansion & Scaling Strategy
ForU AI’s next phase focuses on expanding beyond Southeast Asia, targeting markets where:
- AI-integrated commerce → Enhancing AI-driven personalization for e-commerce platforms, driving higher engagement and transaction volumes.
- Decentralized identity adoption → Expanding AI-DID usage across more industries, including finance, healthcare, and content creation.
- Web3-native AI agents → Scaling AI agent deployment for use cases in automated trading, data management, and DAO governance.
- Cross-chain expansion → Integrating ForU AI’s infrastructure with additional blockchains to increase accessibility and network interoperability.
- Enterprise AI solutions → Partnering with businesses to implement AI-driven workflows that optimize decision-making and operational efficiency.
6. Conclusion
ForU AI pioneers the convergence of decentralized technology and artificial intelligence, empowering individuals and communities with autonomous, user-governed AI agents. Unlike traditional AI, these agents operate transparently, leveraging decentralized identities, on-chain economies, and community-driven incentives to think, act, and earn independently. This integration of AI and crypto democratizes access to powerful AI capabilities, once limited to corporations, enabling even small communities to deploy AI-driven solutions.
As AI becomes embedded in decentralized ecosystems, it will enhance governance, finance, and infrastructure, creating self-optimizing networks. Open blockchain data will fuel smarter, community-driven AI innovations, and DAOs could increasingly govern AI agents, blending human oversight with AI execution. The future may see personal AI economies, where individuals monetize AI versions of themselves, and autonomous markets optimizing economic activity with minimal human intervention.
Mass adoption will depend on making AI agents intuitive and accessible, abstracting blockchain complexity for seamless user experiences. Ethical challenges remain, but decentralized governance safeguards against unintended AI behaviors. By integrating AI with Web3, ForU AI is not just creating technology—it is shaping a decentralized, intelligent digital economy where AI agents work for users, scale productivity, and redefine how value is created and distributed.