Ethereum’s Plan to Reclaim the Throne. Pectra Unveiled

Abstract
Ethereum is at a crossroads. Competition from rivals like Solana, BNB Chain, and Avalanche threatens its dominance, demanding a bold response. Solana, in particular, has doubled its code commits, a key indicator of developer activity, from ~50 to ~100 between April 2024 and March 2025, matching Ethereum’s base-layer commits as the latter fell 70% from ~350 to ~100 (Section 4). That response is Pectra, the April 2025 upgrade combining Prague and Electra hard forks for a transformative overhaul. Pectra’s 11 EIPs target Ethereum’s core challenges: fees, scalability, and security. Imagine doubling the capacity of Ethereum’s Layer 2 (EIP-7691), enabling gasless transactions (EIP-7702), and massively upgrading staking (EIP-7251). Early projections showed boosted L2 throughput, DeFi’s $40-50 billion TVL stabilizing, and staked ETH reaching ~25 million. Yet, challenges persist: base-layer contract deployments have plummeted (60,000 to ~10,000, Sep 2022–Mar 2025), ETH’s price shows limited gains, and testnet hiccups raise concerns. Is Pectra enough to secure Ethereum’s future? This report dives deep into the details, analyzing the risks, the rewards, and what’s next for Ethereum, including the future Fusaka upgrade.
Key Takeaways (TL;DR)
- Ethereum’s Growth & Challenge: Handles 1M daily transactions, hosts ~$50B in DeFi, but faces rival L1s (Solana, BNB, Avalanche) with higher TPS and lower fees, losing base-layer contract deployments (60,000 to ~10,000, Sep 2022–Mar 2025). Solana, notably, doubled its code commits from ~50 to ~100 (April 2024–Mar 2025), matching Ethereum’s base-layer commits while leveraging up to 65,000 TPS and $0.01-$0.05 fees (Section 4).
- Pectra’s Purpose: April 2025 upgrade tackles competition, supercharging Ethereum’s L2 ecosystem with boosted scalability, slashed fees, elevated dApp UX, and streamlined staking/DeFi.
- L2 Scalability: Doubles blob capacity (EIP-7691) to 6 per block, projecting L2 TPS gains (e.g., Arbitrum from 23.3 to 46.6), stabilizing fees ($0.001–$0.003 post-Dencun to potentially $0.0005–$0.0015 post-Pectra).
- dApp UX: Paymaster usage, a key indicator of gasless transactions, has jumped from near zero to 11% in previous upgrades. Post-Pectra remains a mystery, but significant leaps are expected, as EIP-7702’s native paymaster support could make gasless transactions a standard feature.
- DeFi & Staking: Lifts staking limit from 32 to 2,048 ETH (EIP-7251), slashes deposit time to 45 minutes, but risks squeezing DeFi liquidity (~$40–50B TVL, Nov 2024) as staking climbs to ~25M ETH.
- Market Effects: Past upgrades have had a muted price impact; ETH holds at $1,893.07 (2 April 2025). Pectra turbocharges L2s to outpace L1 rivals, but sentiment stays cautious.
- Risks & Challenges: Testnet delays (Holesky, Sepolia), centralization risks, and client diversity issues threaten Pectra’s rollout despite Devnet progress.
- Future Outlook: Fusaka (late 2025) will build on Pectra with Verkle Trees and PeerDAS to solidify Ethereum’s digital city leadership.
1. Introduction
Just as a well-run city must constantly rebuild and upgrade its infrastructure to ensure security and prosperity and meet the growing needs of its citizens, so too must a digital city.
Since its genesis, Ethereum has experienced explosive growth, rapidly scaling to handle ~1 million daily transactions and host ~$50 billion in DeFi value. This exponential expansion places immense demands on the network’s infrastructure. To meet these surging demands and ensure smooth operation, Ethereum has been on a journey of continuous evolution, relying on a series of essential upgrades, with Pectra being the latest.
Figure 1: History of Ethereum’s Major Upgrades
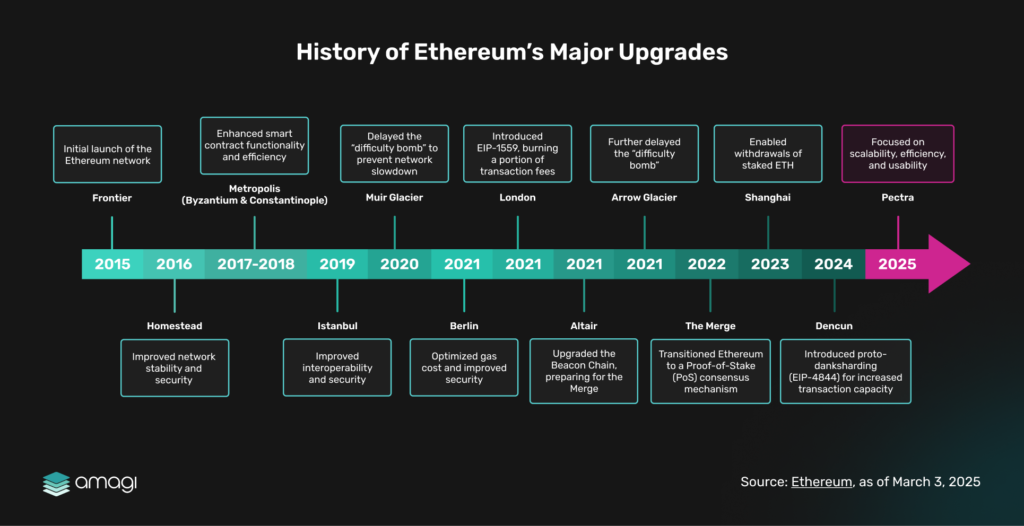
Like the critical infrastructure projects that define a city’s progress, these upgrades are not merely enhancements to address the current strain. They are fundamental necessities, proactively building the robust foundation required to realize Ethereum’s ambitious vision of a new internet. Pectra, the latest infrastructure upgrade to Ethereum’s digital city, represents the next vital step in this ongoing architectural endeavor.
2. Pectra Upgrade Explained
Pectra is an upcoming Ethereum protocol upgrade – a hard fork – that will bring new functionality and changes to both the execution and consensus layers of the network. Pectra aims to address the challenges of transaction fees, scalability, and user experience. Continuing from the growing city analogy, Pectra is like a major city infrastructure overhaul. It’s widening the roads (scalability), optimizing road layouts (efficiency), making public transport more accessible (user experience), and improving the stability of the city’s banking infrastructure (staking).
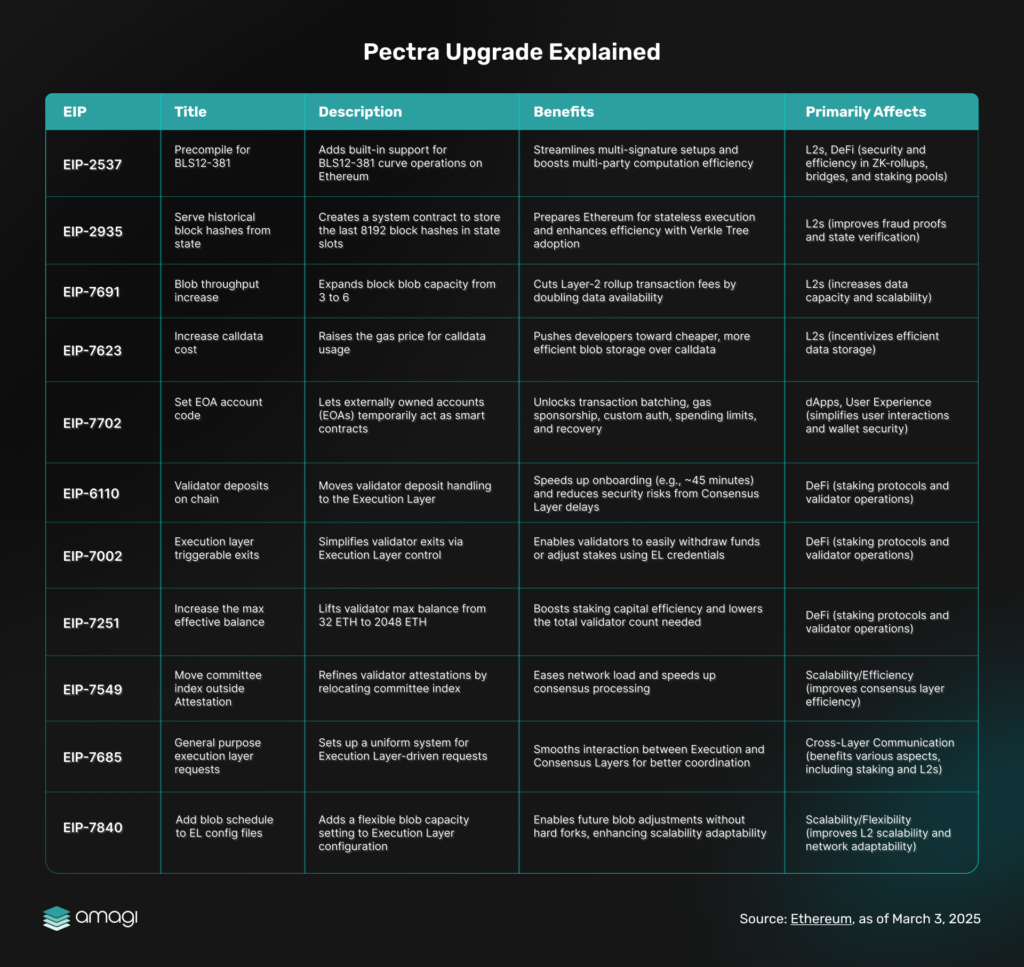
The name Pectra is a combination of Prague, the execution layer hard fork, and Electra on the consensus layer fork, both of which will be activated at the same time. The Prague upgrade focuses on enhancements to the execution layer, where smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) operate. Meanwhile, the Electra upgrade concentrates on improvements to the consensus layer, which is responsible for the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism and overall network security. Pectra brings the most EIPs of any previous upgrade, introducing 11 critical enhancements that tackle transaction fees, boost scalability, and elevate the user experience across both layers of Ethereum’s evolving network.
Figure 2: Pectra Upgrade Explained
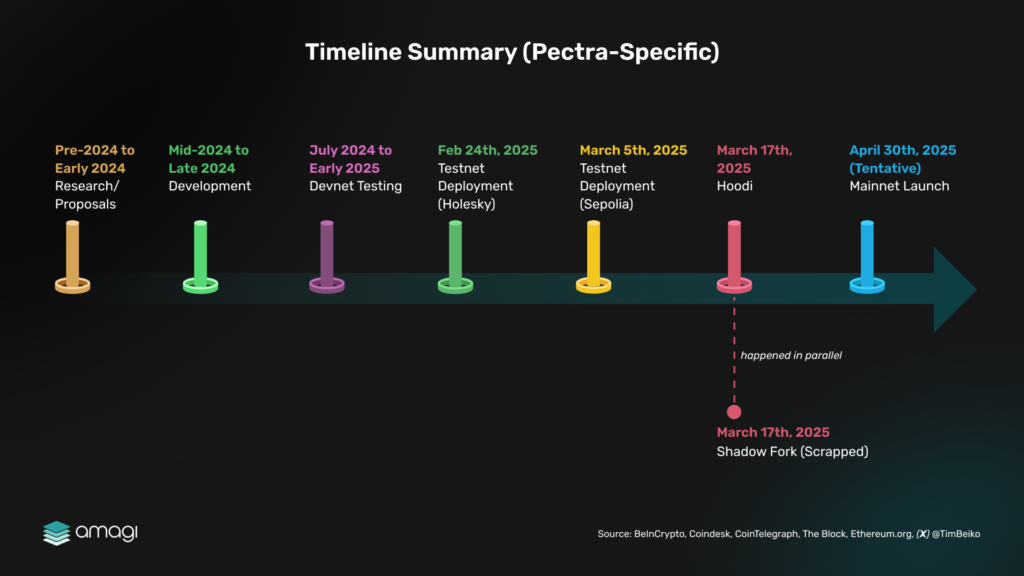
Originally planned for late 2024, Pectra’s launch was delayed to April 2025 due to its extensive scope. The first hiccup occurred in February 2025 when the Pectra upgrade launched on the Holesky testnet but failed to “finalize” (confirm transactions as permanent). The second hiccup happened in March 2025. After a seemingly successful Sepolia testnet, some execution layer clients stopped including transactions in blocks due to a custom deposit contract bug. This halted transaction processing for hours until a fix was deployed. As a solution, during the All Core Developers (ACD) call on March 6, developers decided to create a “shadow testnet”—a temporary parallel network forked from Holesky. Following Holesky’s recovery on March 11, developers decided to pivot and launch Hoodi — a new standalone testnet — on March 17, 2025. Hoodi provides a dedicated, stable environment for finalizing Pectra’s validator exit testing and ensuring a smooth mainnet rollout. The upgrade is now on track for a mainnet deployment, with developers tentatively targeting April 30, 2025.
Figure 3: Timeline Summary (Petra-Specific)
3. Why the Pectra Upgrade is Significant
Ethereum has been facing a narrative of growing competition and questions about its scalability, affordability, and user experience, casting a shadow of fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) over its future dominance. This stems not from external suppression, but from Ethereum’s own slow pace and internal missteps, allowing rivals like Solana and BNB chain to surge ahead with faster, cheaper alternatives—a reality acknowledged by Ethereum Co-Founder Vitalik Buterin, who tweeted on January 18, 2025, “We are indeed currently in the process of large changes to EF leadership structure… some is still in progress,” hinting at internal disarray.
Pectra is Ethereum’s strategic response—a comprehensive upgrade designed to address these self-imposed limitations and elevate its core infrastructure. Drawing a brief inspiration from Prague’s renewal after decades of constraint, Pectra’s 11 EIP upgrades, the most ever, aim to revitalize key sectors, from Layer-2 networks to dApps and DeFi, ensuring Ethereum adapts to reclaim its leadership.
3.1 Enhancing Layer-2 Scalability & Reducing Fees
As the digital city, Ethereum, continues to expand, the need for efficient and affordable transportation becomes paramount. In this context, Layer-2 (L2) networks are akin to high-speed rail lines, designed to alleviate congestion on the main thoroughfares. However, just as a city’s transportation system can face bottlenecks and fluctuating costs, L2s currently grapple with fee variability and scalability limitations.
In this subsection, we’ll explore how the Pectra upgrade doubles blob capacity (EIP-7691) and curbs fee swings (EIP-7623). Two key charts (Figures 4 and 5) illustrate the impact of these enhancements.
Figure 4: L2 Median Fees
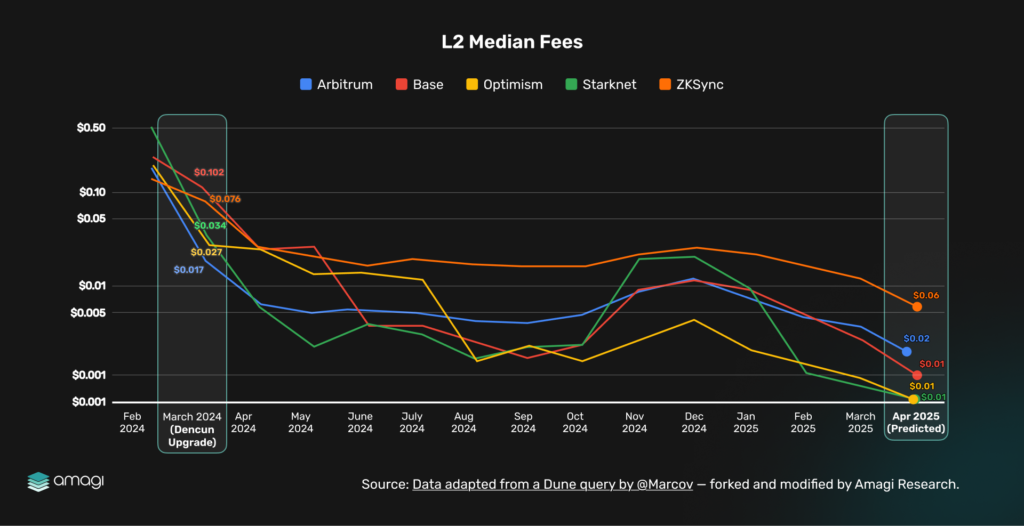
This chart tracks the average ticket prices—transaction fees—on major L2 rail lines, such as Arbitrum, Base, Optimism, Starknet, and zkSync, from February 2024 to April 2025 (projected). In our city analogy, these fees represent the cost of a train ticket for passengers (users) traveling on Ethereum’s high-speed L2 lines. The chart reveals significant fluctuations in ticket prices during the pre-Dencun era, with fares peaking at $0.50–$1.00 during high-demand periods in early 2024, driven by bustling DeFi and NFT activity. For instance, Arbitrum tickets spiked to $0.207 and Optimism to $0.136 in February 2024, much like surge pricing during rush hour in a busy city.
Post-Dencun (March 2024), the introduction of blobs under EIP-4844 acted like a major rail expansion, adding more train cars (three blobs per block) to accommodate passengers, alleviating data scarcity, and dramatically reducing ticket prices to $0.01–$0.03. Optimism’s fares dropped to $0.0065 and Arbitrum’s to $0.023 by April 2024, offering commuters a more affordable ride. However, some variability persists, as if certain train lines still face occasional delays or demand spikes, pushing passengers toward rival transit systems—competing L1s like Solana and BNB Chain—where tickets cost a steady $0.01–$0.05. With Pectra’s EIP-7623, expected to roll out in July 2025, and the doubling of blob capacity via EIP-7691 (from three to six blobs per block), the chart projects a further reduction and stabilization of transaction costs.
In our city analogy, this upgrade is like doubling the number of train cars on each L2 line, ensuring more seats for passengers and reducing competition for space. While the idea that Pectra “stabilizes variability” is a logical conclusion rather than a direct statement, it is inferred from the mechanics of blob capacity and Dencun’s precedent: more train capacity means fewer bottlenecks and more predictable fares. The increased capacity is anticipated to ease transaction bottlenecks, reducing costs by mitigating data scarcity, just as more trains prevent overcrowding during peak hours.
Drawing from Dencun’s precedent—where adding three train cars (blobs) led to an 89–96% fare reduction (e.g., Optimism from $0.207 to $0.023). Pectra’s doubled blob capacity is poised to further lower costs starting April 2025. Using March 2025 transaction fees as a baseline—already reduced by prior upgrades—a conservative 50% cut is projected post-upgrade, tempered by diminishing returns and a practical floor of $0.0005–$0.001, akin to a minimum fare to sustain operations. For example, Optimism’s current $0.001 fee (March 2025) could drop to $0.0005 by April 15, 2025, while Arbitrum’s $0.003 might fall to $0.0015. These costs are expected to stabilize in the weeks following Pectra’s launch, as doubled blob capacity absorbs initial Layer-2 demand without pushing fees below the operational minimum.
Figure 5: L2s TPS: Pre-Pectra vs Post-Pectra (Estimated)

Building on Ethereum’s ongoing renewal, Pectra’s doubling of blob capacity from 3 to 6 per block (EIP-7691), set for April 2025, acts as a major expansion of our digital city’s L2 rail lines, boosting throughput for Optimistic Rollups like Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism. These high-speed routes rely on L1 data availability to handle transaction batches efficiently, and this upgrade promises to ease congestion further. The chart above tracks the TPS – Transactions per second across these lines, comparing pre-Pectra levels (March 14, 2025) to post-Pectra projections with a 2x conservative estimate and an adjusted maximum.
Pre-Pectra, Arbitrum runs at 23.3 TPS, Base at 88.6, and Optimism at 8.78—current limits shaped by today’s 3-blob setup. Post-Pectra, we estimate a conservative 2x boost—doubling to 6 blobs could double throughput if demand aligns—yielding 46.6, 177.2, and 17.56 TPS, respectively. This 2x is cautious, as Dencun’s 3-blob jump didn’t triple TPS (e.g., Arbitrum rose ~45%), hinting at bottlenecks like sequencer speed.
For a peak scenario, we scale to Pectra’s max 9-blob capacity (a 3x data ceiling), adjusted for each L2’s practical limits: Arbitrum hits 69.9 TPS, Base caps at 203.8 (near its 160 TPS record), and Optimism reaches 26.34—akin to a fully loaded transit system at rush hour.
While both Optimistic and zk-Rollups are Layer 2 solutions, Pectra’s increased blob capacity offers more direct benefits to Optimistic Rollups. This is because Optimistic Rollups post transaction data directly to Ethereum’s Layer 1, making blob capacity a critical factor in their scalability. By contrast, zk-Rollups rely on zero-knowledge proofs to compress data off-chain, reducing their dependence on blob space and relying more on cryptographic efficiency and user adoption to scale. For this reason, our analysis highlights the scalability boost for Optimistic Rollups, where Pectra’s impact is most significant—ensuring Ethereum’s expanding rail network can meet its growing demand.
3.2 Improving User Experience and Empowering dApps
As Ethereum’s digital city expands, Pectra’s renewal upgrades its L2 rail stations with more than just added trains (EIP-7691’s blob doubling). EIP-7702, a highly anticipated upgrade, allows externally owned accounts (EOAs) to function temporarily as smart accounts, enabling transaction batching, gas sponsorship, alternative authentication, programmable spending controls, and account recovery mechanisms.
While EIP-7702 is not yet implemented, it builds on the vision of account abstraction laid out by EIP-4337, which is already live. EIP-4337 enables smart contract wallets that can offer gasless transactions using a system called paymasters — smart contracts that sponsor users’ gas fees. However, EIP-4337 operates through a separate infrastructure layer, requiring wallet deployment and a dedicated mempool.
EIP-7702 aims to simplify this by integrating abstraction capabilities directly into Ethereum’s transaction flow. EOAs would be able to access paymaster-sponsored gasless transactions natively, without needing smart wallet deployments or infrastructure overhead. This makes gasless UX more composable, secure, and developer-friendly — opening the door for broader adoption across dApps.
Figure 6: Paymaster Percentage of Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism
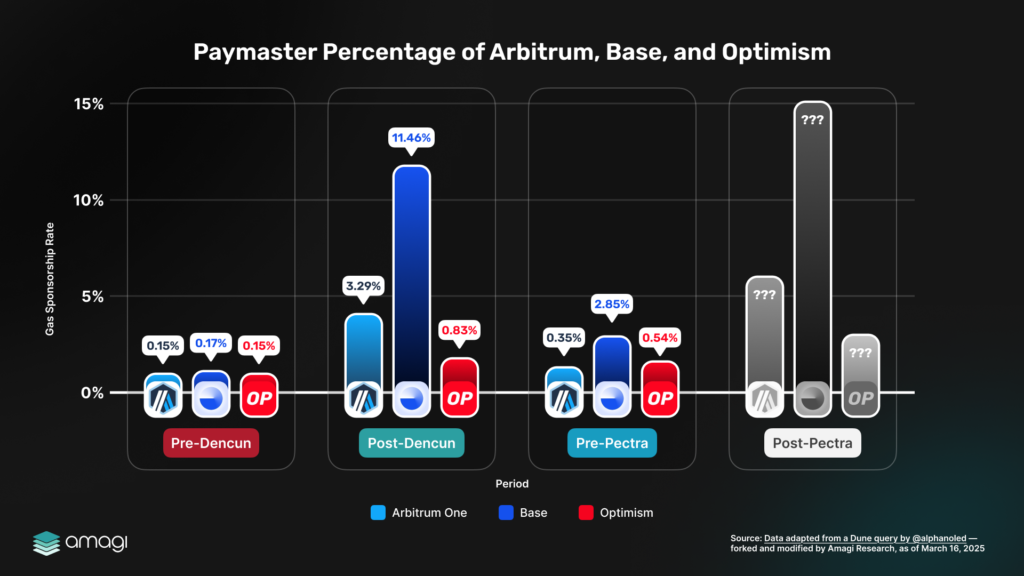
The chart above tracks paymaster usage — a key mechanic that allows third parties to sponsor gas fees on behalf of users. While current paymaster usage is powered by EIP-4337, EIP-7702 is expected to deepen and streamline this functionality at the protocol level. The chart thus serves as a baseline to evaluate future growth once EIP-7702 is live.
Before Dencun (2023), paymaster usage was nearly nonexistent, hovering between 0.15% and 0.17% across Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism, as gasless functionality was limited. Post-Dencun (2024), early adoption of account abstraction pushed usage to 3.29% on Arbitrum, 0.83% on Base, and 0.35% on Optimism, signaling a growing interest in gasless experiences. By pre-Pectra (March 2025), this climbed further to 11.46% (Arbitrum), 2.8% (Base), and 0.54% (Optimism), reflecting steady progress.
Post-Pectra projections remain uncertain, but significant leaps are expected, as EIP-7702’s native paymaster support could make gasless transactions a standard feature.
zk-Rollups (e.g., Starknet, ZKsync) are excluded from this analysis, as their scalability is more reliant on cryptographic proof systems and adoption curve than on L1 data throughput. Focusing on Optimistic Rollups here helps isolate where Pectra’s impact on user experience will be most immediately felt.
3.3 Streamlining DeFi and Staking
In Ethereum’s digital city, staking serves as treasury vaults, securely storing wealth through validator oversight, while DeFi thrives as bustling trade halls, fostering economic exchange with lending, trading, and yield farming. The Pectra upgrade modernizes these vaults with greater efficiency, introducing a new validator type (0x02) for simplified large-scale staking and auto-compounding benefits without pool reliance. The upgrade also reduces the time from deposit to validator activation to just 45 minutes, significantly improving staking UX.
Figure 7: ETH Staked Over Time Since The Merge
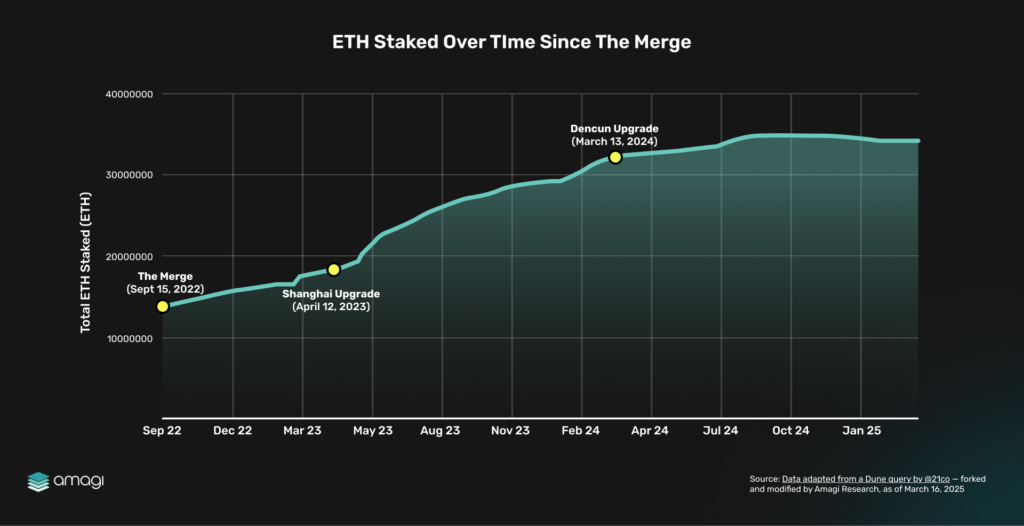
Starting at ~14 million ETH in September 2022, staking surged to ~25 million ETH by November 2024, reflecting growing confidence in Ethereum’s staking ecosystem. Key protocol upgrades drove this rise: the Shanghai Upgrade (April 2023) enabled withdrawals, boosting participation, while Dencun (March 2024) lowered fees, making staking more accessible. Looking ahead, Pectra’s EIP-7251 – which raises the validator cap from 32 to 2,048 ETH – could further encourage high-value deposits, much like a city upgrading its financial reserve infrastructure to accommodate larger treasuries.
Figure 8: Ethereum DeFi TVL

DeFi TVL peaked at ~$60 billion in early 2022, dropped to ~$30 billion post-Merge (September 2022) amid market downturns, recovered to ~$50 billion post-Shanghai Upgrade (April 2023) as withdrawals freed up ETH, and stabilized at ~$40-50 billion by November 2024. This trend often inversely correlates with staking surges—when more ETH fills the treasury vaults, less is locked into validators, and less circulates through DeFi markets, tightening capital availability for lending and trading, a dynamic seen again post-Dencun.
Figure 9: Pectra DeFi Upgrades
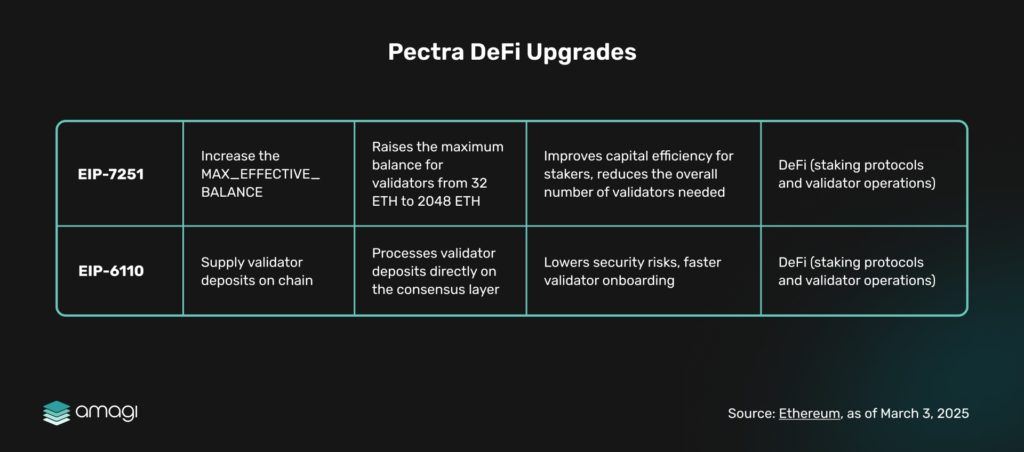
Pectra’s staking enhancements, which streamline large deposits (EIP-7251) and accelerate validator activation (EIP-6110), have the potential to deepen the vaults’ reserves. However, this might also draw liquidity away from DeFi’s commerce, similar to how a city might prioritize financial storage over vibrant market activity. To remain competitive, DeFi protocols may need to adapt by offering more attractive yield opportunities.
4. Ecosystem and Market Effects
In Ethereum’s digital city, Pectra emerges as a strategic renovation to counter rival cities’ growth, aiming to remain competitive by enhancing scalability, reducing transaction fees, improving security, and elevating the developer experience. Facing competition from blockchains like Solana, BNB Chain, and Avalanche, which often boast higher base-layer TPS, Ethereum leverages Pectra to amplify L2 throughput—where most scaling occurs—while its base layer remains at ~15-30 TPS.
4.1 Monthly Contract Deployments & Code Commits
Figure 10: Monthly Contract Deployments: Ethereum vs Rival L1s (Sep 2022 – March 2025)
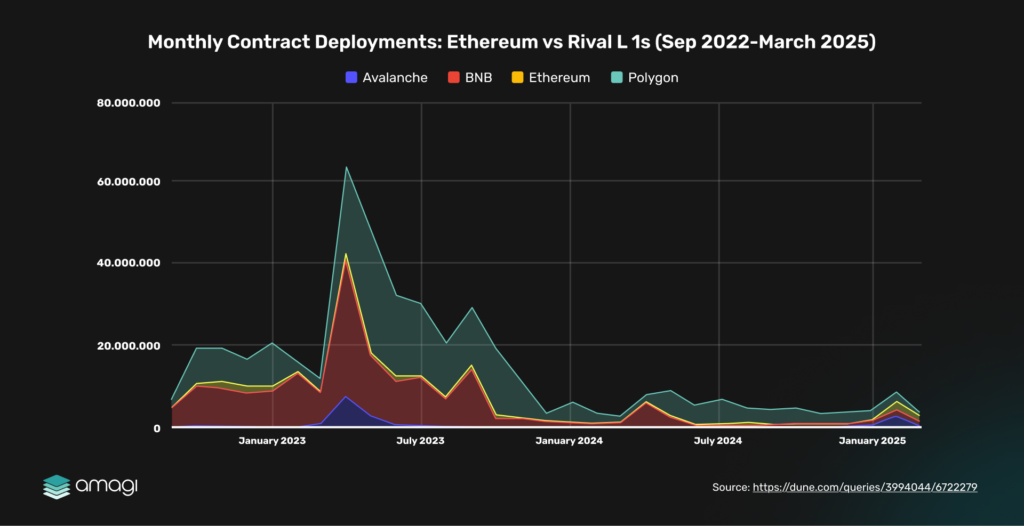
Note: The Ethereum data in this chart reflects only base-layer (L1) contract deployments and does not include Layer 2 (L2) networks like Arbitrum, Polygon zkEVM, or Optimism, as L2 data is often tracked separately due to their distinct scaling role.
Ethereum’s dominance in base-layer contract deployments peaked at ~60,000 in July 2023, driven by DeFi and NFT booms, but declined to ~10,000 by March 2025, reflecting a loss of builder activity to rivals. This exclusion of L2s highlights Ethereum’s challenge at the base layer, where rival L1s like Polygon and BNB Chain saw steady growth, peaking at ~30,000 and ~20,000, respectively, around mid-2023, leveraging lower costs and higher TPS (e.g., Polygon’s ~65 TPS).
Arbitrum, as an L2, surged post-Dencun (March 2024), reaching ~15,000 deployments by March 2025, benefiting from Ethereum’s L2 scalability improvements. This trend underscores Ethereum’s strategic shift: Pectra aims to narrow the gap by boosting L2 scalability (e.g., Arbitrum’s TPS rose from 23.3 to 46.6, per Section 3.1), but its base-layer activity remains vulnerable to rival L1s’ advantages.
Monthly Code Commits: Ethereum vs. Solana (April 2024–March 2025)
While the previous section highlighted Ethereum’s base-layer contract deployment trends compared to L1s like Polygon and BNB Chain, comparable data for Solana’s contract deployments is unavailable due to its distinct program deployment model. To bridge this gap and assess Solana’s developer activity, we turn to monthly code commits. A key indicator of active development. The chart below tracks code commits for Ethereum and Solana from April 2024 to March 2025, offering a direct comparison of their builder engagement.
Figure 11: Code Commits: Ethereum vs Solana
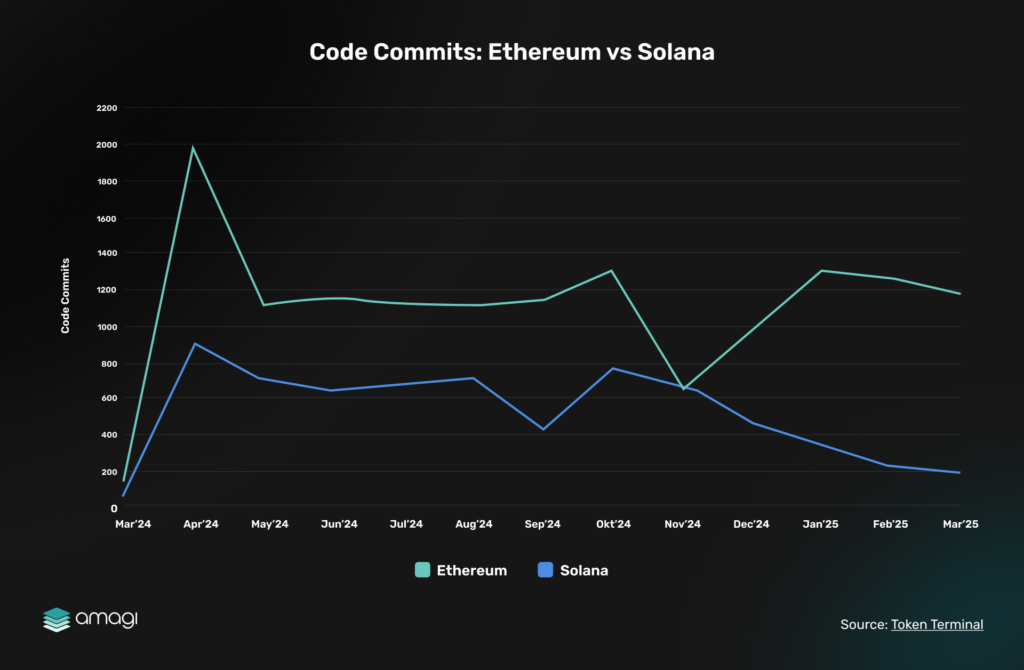
Ethereum’s base-layer commits (green) peaked at ~350 in April 2024 but fell 70% to ~100 by March 2025, reflecting a slowdown in core development as focus shifts to L2s post-Dencun. In contrast, Solana (blue) doubled its commits from ~50 to ~100 over the same period, matching Ethereum’s current level and signaling a surge in developer interest.
Solana’s high TPS (up to 65,000) and low fees ($0.01-$0.05) make it a compelling alternative for builders seeking performance, while Ethereum’s base-layer stagnation—despite L2 scaling (e.g., Arbitrum’s TPS at 23.3, per Section 3.1)—underscores its challenges. Pectra aims to counter this by supercharging L2 scalability, but Solana’s developer momentum poses a competitive threat to Ethereum’s builder mindshare.
4.2 ETH Price Performance after Upgrades
Figure 12: ETH Price Performance After Upgrades
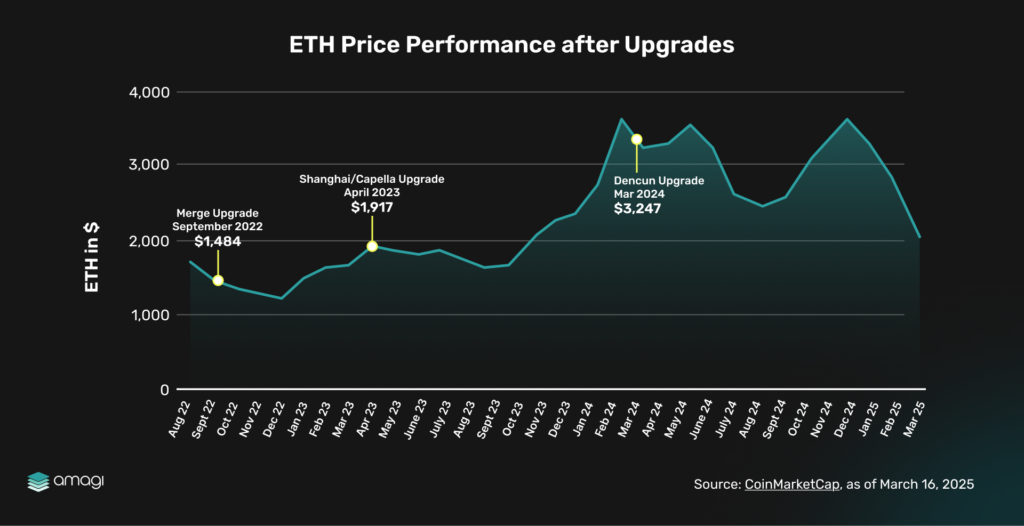
ETH’s price rose from $1,484 post-Merge (September 2022) to $1,989 post-Shanghai (April 2023), peaking at $3,329 by November 2024, driven by market trends and Dencun’s fee reductions (March 2024). However, it dipped to $2,083 by March 2025, reflecting broader market volatility. Historical upgrades like Shanghai and Dencun show minimal direct price impact, suggesting Pectra’s short-term financial effect may be muted, though long-term ecosystem growth could bolster ETH’s value.
4.3 Sentiment and Progress
Pectra’s announcement has sparked mixed sentiment. Industry leaders like Terence Tsao (@terencechain) on X (October 29, 2024) highlighted progress, noting “Pectra Devnet 5 is live,” but community sentiment, per Kaito metrics, remains cautious due to testnet hiccups (e.g., Holesky’s split, per The Block). News headlines reflect this duality—Cointelegraph (March 2025) warns of centralization risks, while others praise scalability gains (@haydenzadams on X, Feb 15, 2025).
5. What’s Next?
Looking ahead, the Fusaka upgrade, slated for late 2025, will build on Pectra’s advancements, introducing Verkle Trees and PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling) to further scale and strengthen Ethereum’s digital city. These features aim to enhance Ethereum’s capacity, efficiency, and decentralization, ensuring it remains a leading hub for innovation in the face of growing competition from rival blockchains like Solana and BNB Chain.
Verkle Trees replace Ethereum’s current Merkle Tree structure with a more efficient design, combining vector commitments to shrink state proofs significantly (from hundreds to just a few kilobytes). This leap enables stateless clients, allowing nodes to validate transactions without storing the entire blockchain state. For users, this means faster, lighter apps and lower hardware demands, while developers gain flexibility to build scalable dApps with less reliance on centralized infrastructure.
PeerDAS supercharges Ethereum’s L2 scalability by optimizing data handling. Extending Pectra’s blob doubling (EIP-7691), PeerDAS allows nodes to sample random chunks of L2 data rather than downloading everything, verifying availability via a distributed network. This triples blob capacity to 18 per block and slashes transaction fees below Pectra’s range.
6. Conclusion
As Ethereum’s digital city stands at a crossroads, Pectra emerges as a pivotal infrastructure upgrade designed to reinforce Ethereum’s leadership amidst fierce competition from rival chains. From its explosive growth, handling ~1 million daily transactions and hosting ~$50 billion in DeFi value. Ethereum has evolved through critical upgrades like the Merge, Shanghai, and Dencun, each laying the foundation for scalability, security, and user experience. Pectra, with its unprecedented 11 EIPs, widens the roads of Layer 2 scalability, optimizes the layouts of dApp usability, and fortifies the treasury vaults of staking, ensuring the city can meet the surging demands of its citizens: developers, stakers, and DeFi users alike.
Yet, the path forward is not without challenges. Testnet hiccups on Holesky and Sepolia, centralization risks, and declining base-layer dominance, exacerbated by Solana’s surging developer activity (doubling code commits to match Ethereum’s ~100 by March 2025, Section 4), signals the urgency of Pectra’s mission. While ETH’s price shows muted responses to past upgrades, the ecosystem’s long-term vitality, boosted by L2 throughput, dApp innovation, and DeFi adaptability, holds promise. Mixed sentiment, from cautious community feedback to optimistic industry voices, reflects both the stakes and the potential. Pectra positions Ethereum to reclaim its leadership, not by outpacing rivals’ base-layer TPS but by enhancing its high-speed L2 rail lines and trade halls, narrowing the gap with competitors like Solana and BNB Chain.
Looking ahead, Fusaka, projected for late 2025, promises further expansion, reinforcing Ethereum’s digital city as a hub of innovation. With this strategic overhaul, Ethereum paves the way to reign supreme, provided it navigates its risks and adapts to the evolving landscape of its digital realm.